Originally published on aimultiple.com
After the COVID-19 pandemic, digital adoption is accelerating in almost every industry and manufacturing is no exception. According to the 2021 Digital Transformation Assessment study conducted by IBM and The Manufacturer, 67% of manufacturers have accelerated digital projects after COVID-19. We explore how digital technologies affect manufacturing with key technologies and trends.
What does digital transformation mean for manufacturing?
Digital transformation in manufacturing involves integrating digital technologies into processes and products to increase manufacturing efficiency and quality.
Digital transformation in manufacturing focuses on:
-
- Improving operational efficiency and reducing costs
- Ensuring the quality of manufactured products
- Responding faster to the changing market requirements and customer demands
Why is digital transformation in manufacturing important now?
Customer expectations and increased competition are the main drivers of digital transformation in manufacturing as with other industries. By leveraging digital technologies, manufacturers can improve speed and efficiency, increase production, decrease costs, and provide a better customer experience.
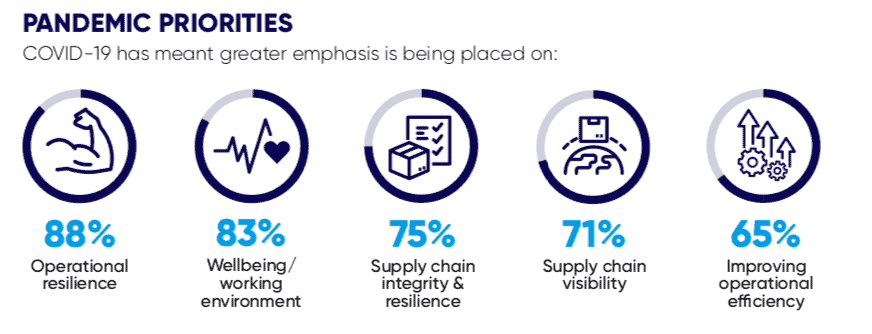
COVID-19 has also demonstrated the importance of embracing digital technologies in manufacturing. Throughout the pandemic, manufacturers faced operational challenges that illuminated the weaknesses in their existing businesses. For instance, having real-time data about the supply chain could enable manufacturers to respond faster to supply shortages and demand spikes during the pandemic. The image below from IBM and The Manufacturer’s study shows the strategies manufacturers focused on during the pandemic and all could benefit from digital technologies.
What are the key technologies and trends enabling digital transformation in manufacturing?
Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytical techniques are involved in most of the digital transformation applications in manufacturing. Specific technologies and trends include:
Robotics
Manufacturing robots automate repetitive tasks, reduce the margin of error, and free up human workers’ time for more productive tasks. AI-enabled robots can train themselves to improve their performance. These robots can be fully autonomous or automate some tasks while working safely alongside human workers. The second type of industrial robots are called collaborative robots (cobots).
IIoT
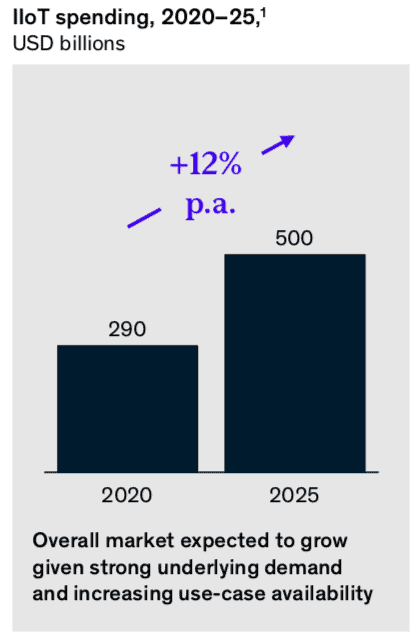
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a sub-category of Internet of Things (IoT) that focuses on applications in industrial sectors. IIoT technology is transforming the manufacturing sector by enabling businesses to monitor the production process in real-time and helping them to make more data-driven decisions with manufacturing analytics. McKinsey predicts that IIoT will be a $500 billion market by 2025. Benefits of IIoT technologies include:
-
- Predictive maintenance
- Energy efficiency of individual machines
- Demand forecasting
- Supply chain visibility
Digital Twins
A digital twin is a digital representation of physical entities such as products, devices, or systems that enable businesses to make model-driven decisions. Digital twins have a wide range of applications in manufacturing including:
-
- Product development
- Design customization
- Shop floor performance improvement
- Predictive maintenance
- Logistics optimization
3D Printing
3D printing technology, also called additive manufacturing, helps businesses to produce complex objects cheaper and faster. Product prototyping is one of the most common use cases of 3D printing in manufacturing, but applications are not limited to it.
Traditional manufacturing is cost-effective in the case of mass production but 3D printing is ideal if a product is not going to be produced in large volumes. 3D printing also offers a cost-effective way to produce customized products or product parts for consumer goods. 3D printing can use a variety of materials including metal.
Augmented and virtual reality
According to PwC, augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) technologies have the potential to add $1.5 trillion to the global economy by 2030. Applications of AR/VR in manufacturing include:
-
-
- Fast prototyping by enabling manufacturers to see how a product would look like without physically creating it.
- Inventory management involves processes that cannot be automated 100%. AR/VR-enabled devices can instruct human workers in a warehouse and provide information about items on shelves.
- Maintenance: Different machines require different maintenance processes and having maintenance instructions accessible in your glasses makes maintenance significantly easier.
-